Originally started from China in December 2019, the Novel Coronavirus or COVID-19, infected 18.1 million people worldwide.
Declared as the pandemic illness by the World Health Organisation (WHO) the Coronavirus is lethal in transmission with an adverse effect on humans. Though the symptoms of the Novel Coronavirus is basic cough and cold or zero symptoms.
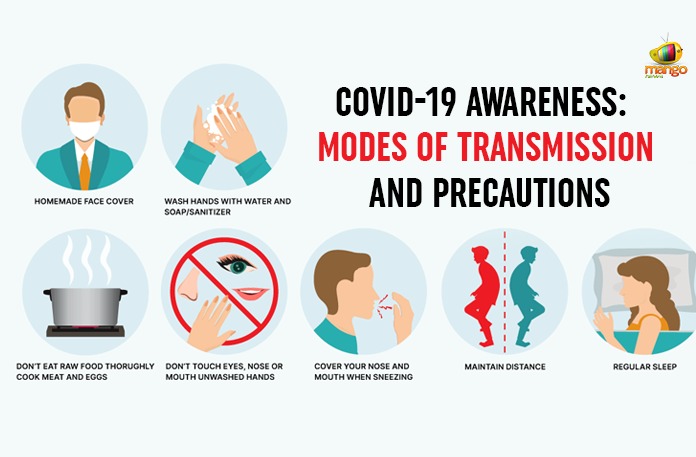
Speaking about the transmission, the disease is lethal in transmission and transmit easily through sneeze and cough.
What is COVID-19?
The Novel Coronavirus is a family of viruses which has an adverse effect on people and have no proven cure till date.
Modes of transmission:
Due to lack of sufficient information about the virus characteristics, doctors suggest that the coronavirus is probably transmitted like other infectious diseases, through:
Direct contact with the droplets dispersed when a patient coughs or sneezes.
Indirect contact by touching surfaces or objects contaminated with the virus and then touching the nose, eyes or mouth.
Direct contact with infected people, animals and their products.
Since COVID-19 is said to be an airborne disease, the chances of transmission is 20% to 23 %.
Based on WHO report, modes of COVID-19 transmission:
Suggested as respiratory infections, COVID-19 also could be transmitted through droplets of different sizes:
when the droplet particles are >5-10 μm in diameter they are referred to as respiratory droplets, and when then are <5μm in diameter, they are referred to as droplet nuclei.1.
According to current evidences, COVID-19 virus is primarily transmitted between people through respiratory droplets and contact routes.
Droplet transmission occurs when a person is in in close contact (within 1 m) with someone who has respiratory symptoms (e.g., coughing or sneezing) and is therefore at risk of having his/her mucosae (mouth and nose) or conjunctiva (eyes) exposed to potentially infective respiratory droplets. Transmission may also occur through fomites in the immediate environment around the infected person.8 Therefore, transmission of the COVID-19 virus can occur by direct contact with infected people and indirect contact with surfaces in the immediate environment or with objects used on the infected person (e.g., stethoscope or thermometer).
Airborne transmission is different from droplet transmission as it refers to the presence of microbes within droplet nuclei, which are generally considered to be particles <5μm in diameter, can remain in the air for long periods of time and be transmitted to others over distances greater than 1 m.
In the context of COVID-19, airborne transmission may be possible in specific circumstances and settings in which procedures or support treatments that generate aerosols are performed; i.e., endotracheal intubation, bronchoscopy, open suctioning, administration of nebulized treatment, manual ventilation before intubation, turning the patient to the prone position, disconnecting the patient from the ventilator, non-invasive positive-pressure ventilation, tracheostomy, and cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
COVID-19 symptoms:
Since COVID-19 is a viral illness, isolation may help to contain the spread of the virus.
People who are unsure about COVID-19 test and get symptoms like fever, cough, sore throat, shortness of breath for 2-4 weeks should assume it to be Coronavirus infection and self isolate until tested negative.
Some people could also have symptoms of body aches, and/or diarrhea.
Precautions or self isolation:
While self isolation you need to be at home, get rest, drink plenty of healthy fluids (like water, Gatorade.)
In addition, you should wash your hands often for 20 seconds with soap and water, use an alcohol based hand sanitizer that contains at least 60% alcohol and keep yourself under an hygienic environment.
High priority times to wash hands include:
After blowing your nose, coughing, or sneezing
After using the restroom, before eating or preparing food, after contact with animals or pets, before and after providing routine care for another person who needs assistance, such as a child.
To get relief from pain, one can rely on Tylenol (acetaminophen) pain relievers, fever reducers, decongestants and cough medicine to manage symptoms.
However, it is always safe to consult a chemist and doctor before taking any medications.
Do not go to work/school/public areas, it could spread the virus.
Avoid public transportation/ride-sharing/taxis.
Separate yourself from other people and animals in your home, particularly people with special vulnerability to COVID-19 infection like senior citizens (65 or older,) those with immune compromise and health care workers and children.
Do not welcome visitors into your home.
Use a separate bathroom, if available, and separate towels, utensils and bottles.
Cover your coughs and sneezes with the inside of your elbow or with a tissue, throwing the tissue away immediately afterwards.
People previously diagnosed with COVID-19 should wear a face mask when around other people if they are still having symptoms.
Clean high-touch surfaces every day with disinfectant, such as countertops, tables, doorknobs, toilets and computer keyboards.
Please check your temperature and monitor your symptoms daily.
Seek prompt medical care if you feel like you are getting worse.
Some of the worst medical condition which might need medical attention could be:
High fever, shortness of breath or difficulty breathing (feeling like you can’t get enough air, gasping, unable to speak without stopping for air, feelings of distress,) weakness, dizziness or chest pain.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, please call your primary doctor before seeking care or helpline numbers of your respective area.
The Novel Coronavirus has infected a large number of people in Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu and Delhi, Telangana and Andhra Pradesh.
The everyday spike in these regions of India are not only a matter of concern for respective governments, but also a serious issue related to the citizens.
Since, COVID-19 has no proven cure, medication or vaccine, one should keep their immunity strong, follow social distancing and wear masks.
Wearing face masks could reduce 80 % to 90 % chance of being infected or infecting others.
In addition, hand sanitizer and washing hands every 15 minutes is another helpful and easy way to prevent being infected by the virus.
Stay tuned for further details of the Novel Coronavirus.